DJI GEO System Tutorial
If you come across any mistakes or bugs in this tutorial, please let us know by sending emails to dev@dji.com. Please feel free to send us Github pull request and help us fix any issues.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to use the DJIFlyZoneManager and DJIFlyZoneInformation of DJI Mobile SDK to get the fly zone information, and unlock authorization fly zones.
You can download the tutorial's final sample project from this Github Page.
We use Mavic Pro as an example to make this demo. Let's get started!
Introduction
The Geospatial Environment Online (GEO) system is a best-in-class geospatial information system that provides drone operators with information that will help them make smart decisions about where and when to fly. It combines up-to-date airspace information, a warning and flight-restriction system, a mechanism for unlocking (self-authorizing) drone flights in locations where flight is permitted under certain conditions, and a minimally-invasive accountability mechanism for these decisions.
Application Activation and Aircraft Binding in China
For DJI SDK mobile application used in China, it's required to activate the application and bind the aircraft to the user's DJI account.
If an application is not activated, the aircraft not bound (if required), or a legacy version of the SDK (< 4.1) is being used, all camera live streams will be disabled, and flight will be limited to a zone of 100m diameter and 30m height to ensure the aircraft stays within line of sight.
To learn how to implement this feature, please check this tutorial Application Activation and Aircraft Binding.
Implementing the UI of the Application
Importing SDK and Register Application
Now, let's create a new project in Xcode, choose Single View Application template for your project and press "Next", then enter "DJIGeoSample" in the Product Name field and keep the other default settings.
Once the project is created, let's delete the ViewController.h and ViewController.m files, which were created by Xcode when you create the project. Then create a UIView Controller named RootViewController and set the class of original ViewController object in the storyboard to "RootViewController".
Next, let's import the MapKit.framework and DJISDK.framework to the project and implement the registration process in the RootViewController. If you are not familiar with the process of importing and activating DJI SDK, please check this tutorial: Importing and Activating DJI SDK in Xcode Project for details.
Working on the UI of Application
Creating the UI of RootViewController
Let's open the "Main.storyboard" and make the RootViewController embed in a Navigation Controller and set it as the Storyboard Entry Point. Next, drag and drop two UILabel objects to the RootViewController and named them as "Product Connection Status" and "Model: Not Available". Moreover, drag and drop a UIButton object and place under the two UILabels, named it as "Open", then set its background image as "btn.png" file, which you can get it from the tutorial's Github Sample Project. Lastly, setup the UI elements' auto layout to support multiple device screen size.
Creating the UI of DJIGeoDemoViewController
Drag and drop another ViewController object from the Object Library to the right of RootViewController in the storyboard. Then create another UIViewController class file in the navigator and named it as "DJIGeoDemoViewController", then set the class name in storyboard too.
Furthermore, put a Map View at the bottom of the ViewController and adjust its size as the ViewController view's size.
Then drag and drop 7 UIButton objects and place them on the upper left side, named them as "Login", "Logout", "Unlock", "GetUnlock", "Start Simulator", "Stop Simulator" and "EnableGEO". Moreover, drag and drop two UILabels and place them on the right of the 7 UIButton objects, set the text of them as "LoginState" and "Unknown FlyZone Status". Furthermore, drag and drop a UITableView under the two UILabels and set its data source and delegate to DJIGeoDemoViewController. Lastly, drag and drop a Picker View and two UIButtons, then place them inside a new UIView at the bottom. For more detail configurations of the storyboard, please check the Github sample project. If everything goes well, you should see the following screenshot:
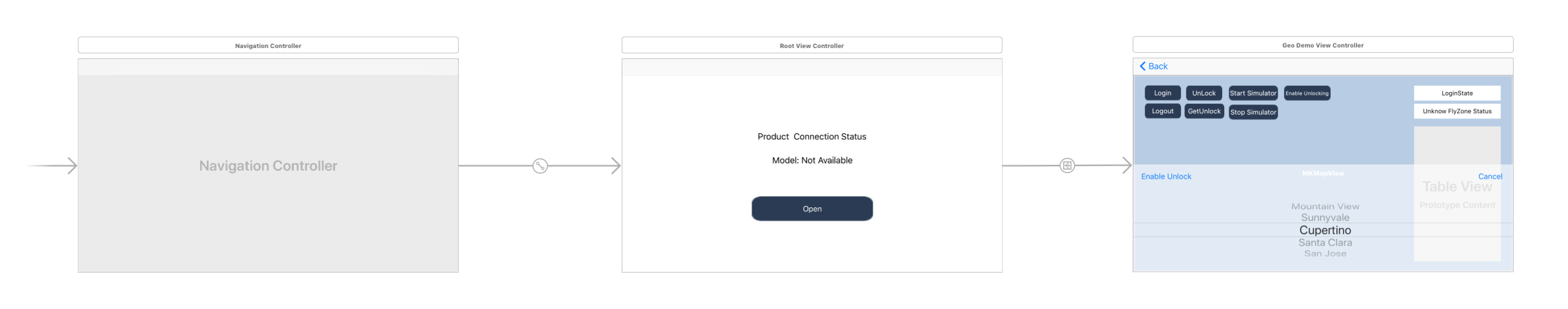
Working on RootViewController
Let's open RootViewController.m file and create IBOutlets properties to link the UI elements in the storyboard. Then add the following method to update the two UILabel objects' content when product connection update:
-(void) updateStatusBasedOn:(DJIBaseProduct* )newConnectedProduct { |
Next, invoke the above method at the end of both the viewDidAppear method and productConnected: method as shown below:
- (void)viewDidAppear:(BOOL)animated |
- (void)productConnected:(DJIBaseProduct *)product |
For more details of the implementation of RootViewController, please check the tutorial's Github sample project.
Implementing Annotation and Overlay on Map View
Working on Aircraft Annotation
Let's continue to add the aircraft annotation on the map to show its position when we are testing the GEO system feature.
Firstly, create a subclass of NSObject and named it as "DJIAircraftAnnotation", replace the code of its header and implementation files as shown below:
- DJIAircraftAnnotation.h
|
- DJIAircraftAnnotation.m
|
In the code above, we implement the MKAnnotation protocol and declare a property of CLLocationCoordinate2D object coordinate, which will be used to store the coordinate data. Then declare a CGFloat property heading, and use it to store the heading value of the aircraft.
Then implement the initWithCoordinate:heading: method in the implementation file.
Once you finish it, let's create a class named "DJIAircraftAnnotationView", which is a subclass of MKAnnotationView, and replace the codes of header and implementation files with the followings:
- DJIAircraftAnnotationView.h
|
- DJIAircraftAnnotationView.m
|
In the code above, we firstly implement the initWithAnnotation:resuseIdentifier: method for initialization and create the updateHeading: method to update the heading of the aircraft annotation view.
For the "aircraft.png" file, please get it from this tutorial's Github sample project and put it in the Assets.xcassets.
Working on FlyZone Circle Overlay
Now, let's add circle overlay with different colors and polygon overlay to represent Fly Zones on the map view.
Create an MKCircle class named "DJIFlyZoneCircle" and implement its header file as shown below:
- DJIFlyZoneCircle.h
|
In the code above, we declare the following variables:
- flyZoneCoordinate property is used to store the coordinate data of the fly zone circle
- flyZoneRadius property is used to store the radius of the fly zone circle in meters
- category property is used to store the category of the fly zone circle
- flyZoneID property is used to store the fly zone's identifier, which is required in the unlock process
- name property is used to store the name of the fly zone.
Next, let's create the DJIFlyZoneCircleView class, which is a subclass of MKCircleRenderer, and replace the codes with the followings:
- DJIFlyZoneCircleView.h
|
- DJIFlyZoneCircleView.m
|
In the code above, we implement the following feature:
1. In the header file, we declare the initWithCircle: method for initialization.
2. Then we implement the initWithCircle: method by setting the fillColor and strokeColor of MKCircleRenderer based on the category property value of "DJIFlyZoneCircle":
- Authorization Fly Zone (Yellow Color)
- Restricted Fly Zone (Red Color)
- Warning Fly Zone (Green Color)
- Enhanced Warning Fly Zone (Green Color)
3. Finally, assign the lineWidth property of MKCircleRenderer to "3.0f" to set the fly zone circle's width.
So far, we have finished implementing the aircraft annotation and fly zone overlay, For the polygon fly zone overlay, please check the implementations of the DJIFlyLimitPolygonView and DJIPolygon classes. For the implementation of subOverlay fly zones, please check the DJILimitSpaceOverlay and DJIMapOverlay classes. You can get these classes from this tutorial's Github sample project.
Now, let's continue to implement the DJIMapViewController to add the fly zone overlay and subOverlay on the Map View.
Implementing DJIMapViewController
Adding and Updating Aircraft Annotation on the Map View
Here, we may need to create a Map View to show the map and draw the fly zone circles and aircraft on it. Now create a new ViewController class named "DJIMapViewController" and then open the DJIMapViewController.h file and replace the content with the followings:
|
In the code above, we implement the following features:
- Create an NSMutableArray property and named it as
flyZonesto storeDJIFlyZoneInformationobjects. - Create the initialization method
initWithMap:for DJIMapViewController - Create the
updateAircraftLocation:withHeading:method to update the aircraft's location and heading on the map view - Add the
refreshMapViewRegionmethod to refresh the map view's region - Add the
updateFlyZonesInSurroundingAreamethod to update the fly zones in the surrounding area of aircraft; - Lastly, add the
fetchUpdateFlyZoneInfomethod to fetch the updated fly zone info strings.
Next let's implement the initWithMap: and updateAircraftLocation:withHeading: methods in the DJIMapViewController.m file.
Firstly, we should create a CLLocationCoordinate2D property, a DJIAircraftAnnotation property and a MKMapView property, then implement the MKMapViewDelegate protocol in the class extension part as shown below:
|
Next, implement the two methods as shown below:
- (id)initWithMap:(MKMapView*)mapView{ |
In the code above, we implement the following features:
-
In the
initWithMap:method, we initialize the DJIMapViewController by passing the MKMapView object "mapView", then store it to themapViewproperty and set themapView's delegate to DJIMapViewController. -
In the
updateAircraftLocation:withHeading:method, we firstly check if thecoordinateis valid, then update theaircraftCoordinateproperty. If theaircraftAnnotationproperty is nil, invoke theinitWithCoordinate:heading:method of DJIAircraftAnnotation to create it, then invoke the MKMapView'saddAnnotation:method to add the aircraft annotation on the map. Lastly, adjust the map view's region by invoking thesetRegion:animated:method. -
If the
aircraftAnnotationproperty is not nil, then update its coordinate and the heading of the aircraft annotation view.
Lastly, implement the MKMapViewDelegate method as shown below:
- (MKAnnotationView *)mapView:(MKMapView *)mapView viewForAnnotation:(id <MKAnnotation>)annotation |
Adding Fly Zone Overlay on the Map View
After we have added the aircraft annotation on the map, now let's add some fly zone overlays on the map to show the fly zone visually.
Firstly, import the "DJIFlyZoneCircle.h" and "DJIFlyZoneCircleView.h" header files, then create an NSMutableArray property and named it as 'flyZones' to store the fly zone circle as shown below:
|
For the "DemoUtility.h" file, we will implement it later.
Next, add the following code to initialize the flyZones and mapOverlays arrays and invoke the forceUpdateFlyZones method to force update fly zones at the bottom of initWithMap: method:
self.flyZones = [NSMutableArray array]; |
Moreover, implement the updateFlyZonesInSurroundingArea and updateFlyZoneOverlayWithInfos: methods as shown below:
-(void) updateAircraftLocation:(CLLocationCoordinate2D)coordinate withHeading:(CGFloat)heading |
In the code above, we implement the following features:
-
We invoke the
updateFlyZonesInSurroundingAreamethod in theupdateFlyZonesandforceUpdateFlyZonesmethods to update the fly zones and theupdateFlyZonesmethod will be invoke in theupdateAircraftLocation:withHeading:method when the aircraft location changes. -
In the
updateFlyZonesInSurroundingAreamethod, we invoke thegetFlyZonesInSurroundingAreaWithCompletion:method of DJIFlyZoneManager to get all the fly zones within 20km of the aircraft. If you are using DJISimulator to test the GEO system feature, this method is available only when the aircraft location is within 50km of (37.460484, -122.115312), which is the coordinate of Palo Alto Airport. Then in the completion method, if it gets theinfosarray successfully, we invoke theupdateFlyZoneOverlayWithInfos:method to update the fly zone overlays on the map view. Otherwise, remove the map overlays on the map view and clean up theflyZonesarray. -
In the
updateFlyZoneOverlayWithInfos:method, we firstly create theoverlaysandflyZonesarrays to store theDJILimitSpaceOverlayandDJIFlyZoneInformationobjects. Next, use a for loop to get theDJILimitSpaceOverlayandDJIFlyZoneInformationobjects and store in the arrays.
Furthermore, remove the fly zone overlays on the map by invoking the removeMapOverLays method first and remove objects in the flyZones array. Then
invoke the addMapOverlays methods to new DJILimitSpaceOverlay fly zone overlays on the map and add new DJIFlyZoneInformation objects in the flyZones array.
Finally, let's implement the refreshMapViewRegion method as shown below:
- (void)refreshMapViewRegion |
In the code above, we invoke the setRegion:animated: method of MKMapView to update the region on the map view when the aircraft coordinate changes.
For more details, please check the DJIMapViewController class in this tutorial's Github sample code.
Implementing DJIGeoDemoViewController
Implementing DemoUtility
Before implement the DJIGeoDemoViewController, let's implement the DemoUtility class first to implement some common methods. Create an NSObject class named "DemoUtility" and update the codes in the header file and implementation file as shown below:
- DemoUtility.h
|
- DemoUtility.m
|
In the code above, we mainly create the three methods to fetch the DJIBaseProduct, DJIAircraft, and DJIFlightController objects. Moreover, create an extern function ShowResult to present a UIAlertController for showing messages.
Implementing Login and Logout Features
Now, let's open the DJIGeoDemoViewController.m file and import the following header files and create related IBOutlet properties and IBAction methods to link the UI elements in the storyboard:
|
In the code above, we also create a DJIMapViewController property djiMapViewController and a NSTimer property updateLoginStateTimer to update the loginStateLabel's text content.
Next, let's implement the onLoginButtonClicked: and onLogoutButtonClicked: IBAction methods as shown below:
- (IBAction)onLoginButtonClicked:(id)sender |
Here, we invoke the logIntoDJIUserAccountWithCompletion: method of DJIFlyZoneManager to present a login view controller for users to login their DJI account. Next, we invoke the logOutOfDJIUserAccountWithCompletion: method of DJIFlyZoneManager to logout users's DJI account.
Lastly, in order to update the loginStateLabel with the user account status, we may need to init the updateLoginStateTimer in the viewWillAppear: method as shown below:
- (void)viewWillAppear:(BOOL)animated |
In the code above, we implement the following features:
-
Initialize the
updateLoginStateTimerto invoke theonUpdateLoginStateselector method to update theloginStateLabelcontent in theviewWillAppear:method. -
Set the
updateLoginStateTimerto nil in theviewWillDisappear:method. -
Invoke the
getUserAccountStatusmethod of DJIFlyZoneManager and assign the value to a DJIUserAccountStatus object. Next, use a switch statement to check the value ofstateobject and assign related string content tostateStringvariable. Lastly, updateloginStateLabel's text content with thestateStringvariable value.
Working on DJISimulator Feature
With the help of DJISimulator, you can simulate the coordinate data of the aircraft to some GEO Zone areas for testing without actually flying the aircraft.
Moreover, you can also use the DJISimulator to control the aircraft in a simulated environment based on the virtual stick input, this would be helpful when you are testing if the authorization fly zone is unlocked successfully by trying to take off the aircraft.
Now let's implement the start and stop simulator buttons' IBAction methods as shown below:
- (void)viewDidLoad |
In the code above, we implement the following features:
-
In the
onStartSimulatorButtonClicked:method, we firstly fetch the DJIFlightController object and assign it to theflightControllervariable. Next, create a UIAlertController with the message of "Input Coordinate" and the style of "UIAlertControllerStyleAlert". Moreover, add two textFields and set their placeholder content as "latitude" and "longitude". We will use these two textFields to enter the simulated latitude and longitude data. -
Then we implement the UIAlertAction handler of
startActionand invoke thestartSimulatorWithLocation:updateFrequency:GPSSatellitesNumber:withCompletion:method of DJISimulator to start the simulator by passing thelocationvariable, which is made from the two textFields's content, and 20 as frequency, 10 as GPS Satellites number. If starting simulator successfully without error, invoke therefreshMapViewRegionmethod of DJIMapViewController to update the map view's region and zoom into the new coordinate we just set. Lastly, add the two UIAlertAction variables and present the UIAlertController. -
In the
onStopSimulatorButtonClicked:method, we firstly fetch the DJIFlightController object and then invoke thestopWithCompletion:method of DJISimulator to stop the simulator.
Implementing GEO System Features
Update Fly Zone Info and Aircraft Location
If you want to unlock a fly zone, you may need to get the fly zone's ID first. Now let's update the fly zone info and update the aircraft's location when simulated coordinate data changes.
Implement the DJIFlyZoneDelegate, DJIFlightControllerDelegate, UITableViewDelegate and UITableViewDataSource protocols in the class extension part of DJIGeoDemoViewController and declare the updateFlyZoneDataTimer, unlockFlyZoneIDs, showFlyZoneMessageTableView and flyZoneInfoView properties as shown below:
|
Next, let's refactor the viewDidLoad method and implement the initUI method as shown below:
- (void)viewDidLoad |
In the code above, we set the delegate property of DJIFlightController, DJIFlyZoneManager and DJIFlightController's simulator to self and initialize the isGEOSystemEnabled and flyZoneInfoView properties.
In the viewWillAppear: method, let's add the following code at the bottom to update the fly zones in the aircraft's surrounding area and initialize the updateFlyZoneDataTimer property:
self.updateFlyZoneDataTimer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:4.0f target:self selector:@selector(onUpdateFlyZoneInfo) userInfo:nil repeats:YES]; |
Then in the viewWillDisappear: method, add the following code to set updateFlyZoneDataTimer to nil at the bottom:
if (self.updateFlyZoneDataTimer) |
Furthermore, implement the selector method of onUpdateFlyZoneInfo as shown below:
- (void)onUpdateFlyZoneInfo |
In the code above, we invoke the reloadData method of UITableView to update the fly zone info.
Moreover, let's implement the delegate methods of DJIFlyZoneDelegate and DJIFlightControllerDelegate as shown below:
|
In the code above, we implement the following features:
- In the
flyZoneManager:didUpdateFlyZoneState:delegate method, we use a switch statement to check the DJIFlyZoneState enum value and update theflyZoneStatusLabelcontent. - In the
flightController:didUpdateState:delegate method, we get the updated aircraft location and heading data from the DJIFlightControllerState and invoke theupdateAircraftLocation:withHeading:method of DJIMapViewController to update the aircraft's location and fly zone overlays on the map view.
Lastly, let's implement the delegate methods of UITableViewDelegate and UITableViewDataSource as shown below:
#pragma mark - UITableViewDelgete |
In the code above, we implement the following features:
- In the
tableView:numberOfRowsInSection:delegate method, we return the count of theflyZonesarray of DJIMapViewController. - In the
tableView:cellForRowAtIndexPath:delegate method, we initialize a UITableViewCell object and set itstextLabelcontent as the NSString of DJIFlyZoneInformation's related properties. - In the
tableView:didSelectRowAtIndexPath:delegate method, when user select a specific tableView cell, we will show theflyZoneInfoViewscroll view and update the related fly zone information on thestatusTextViewof the scroll view.
Unlock Fly Zones
Once you finish the above steps, let's implement the unlock fly zone feature. Create the unlockFlyZoneIDs property in the class extension part as shown below:
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableArray<NSNumber *> * unlockFlyZoneIDs; |
Then add the following code to initialize the property in the initUI method as shown below:
self.unlockFlyZoneIDs = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init]; |
Now let's implement the onUnlockButtonClicked and onGetUnlockButtonClicked IBAction methods and the showFlyZoneIDInputView method as shown below:
- (IBAction)onUnlockButtonClicked:(id)sender |
In the code above, we create a UIAlertController with the message of "Input ID", and add a textField with the placeholder of "Input". Then create three UIAlertAction objects for cancel, continue, and unlock actions:
-
Cancel Action
It will dismiss the UIAlertController.
-
Continue Action
It will add the current input fly zone ID to the
unlockFlyZoneIDsarray and present the UIAlertController again. -
Unlock Action
It will add the current input fly zone ID to
unlockFlyZoneIDsarray and invoke theunlockFlyZones:withCompletion:method of DJIFlyZoneManager by passing theunlockFlyZoneIDsarray to unlock fly zones. If unlock fly zone success, invoke thegetUnlockedFlyZonesWithCompletionmethod of DJIFlyZoneManager to fetch the unlock fly zone info. Then, invoke theShowResult()extern function to show a UIAlertViewController to inform the results to the users.
Furthermore, add the three UIAlertAction objects to the alertController and present it. Lastly, in the onGetUnlockButtonClicked method, we invoke the getUnlockedFlyZonesWithCompletion method of DJIFlyZoneManager to get the unlocked fly zones and show an alert view to inform the user.
Enable Unlocked Fly Zone
After unlocking the fly zone, let's continue to implement the feature of enabling the unlocked fly zone. This is useful if the aircraft is shared between users.
Create and add the following properties in the class extension part as shown below:
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIPickerView *pickerView; |
In the code above, we create IBOutlet properties to link the UI elements in the storyboard. Also create the unlockedFlyZoneInfos array property to store the unlocked DJIFlyZoneInformation object. Moreover, create the selectedFlyZoneInfo property to store the selected DJIFlyZoneInformation object. Lastly, create the isUnlockEnable bool property to store the fly zone enable unlocked state.
Once you finished the steps above, let's continue to implement the following methods:
- (void)viewDidLoad |
Here, we hide the pickerContainerView in the viewDidLoad method first and initialize the unlockedFlyZoneInfos property in the initUI method.
Next, add the following code in the onGetUnlockButtonClicked method to add unlocked DJIFlyZoneInformation objects in the unlockedFlyZoneInfos array:
if ([target.unlockedFlyZoneInfos count] > 0) { |
Lastly, implement the following methods:
- (IBAction)enableUnlocking:(id)sender { |
In the code above, we implement the following feature:
-
In the
enableUnlocking:method, show thepickerContainerViewand reload the components of thepickerViewwhen the button is pressed. -
In the
conformButtonActionmethod, invoke thesetUnlockingEnabled:withCompletion:method ofDJIFlyZoneInformationto enable the unlocked fly zone. -
In the
cancelButtonAction:method, hide thepickerContainerViewwhen the cancel button is pressed. -
Implement the delegate methods of
UIPickerViewDataSourceandUIPickerViewDelegatedefine the data source and select row behaviour of thepickerView.
Running the Sample Code
We have gone through a long way so far, now, let's build and run the project, connect the demo application to your Mavic Pro (Please check the Run Application for more details) and check all the features we have implemented so far.
Unlock Authorization Fly Zone Workflow
- Login your DJI account, if it's a new account, you may need to complete the verification process.
- Press ENABLED GEO button to enable the GEO system and restart the aircraft.
- Press Start Simulator button and enter coordinate data to simulate the aircraft's coordinate to the authorization area around Palo Alto Airport (37.460484, -122.115312)
- Wait for a while until the fly zone info updated in the textView on the right side.
- Get the authorization fly zone ID you want to unlock from the textView, which should be level 1
- Press Unlock button and enter the fly zone ID to unlock it
- If you unlock the fly zone successfully, you may notice that the fly zone number and fly zone info are updated on the right textView, and one of the yellow circle will disappear in the map.
Note: Limited Simulation Area
Currently, you can only test the GEO feature within 50km of (37.460484, -122.115312), which is the location of Palo Alto Airport in California, United States.
Login and Logout DJI Account
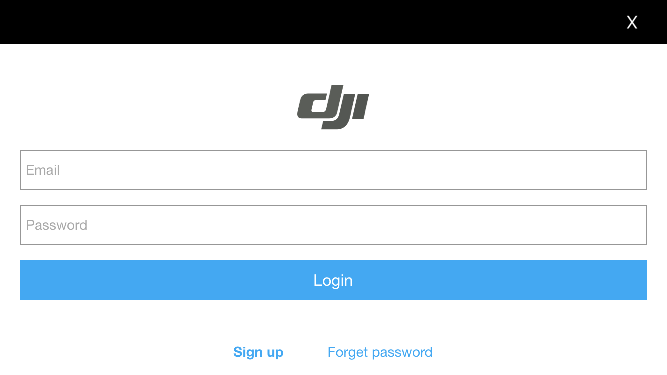
1. Login DJI Account
Press the Login button and a login view controller will pop up as shown below:
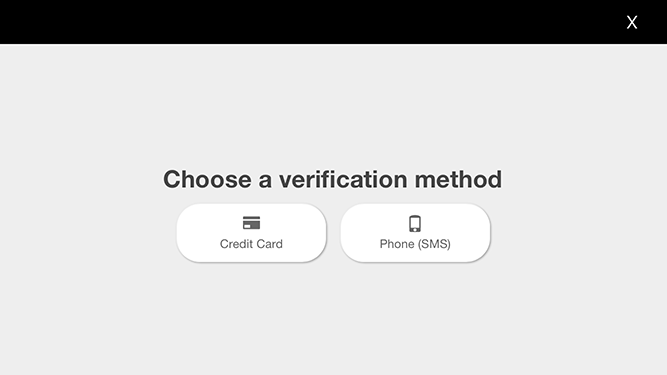
If it's a new DJI account, it will show a verification view as shown below:
2. Logout DJI Account
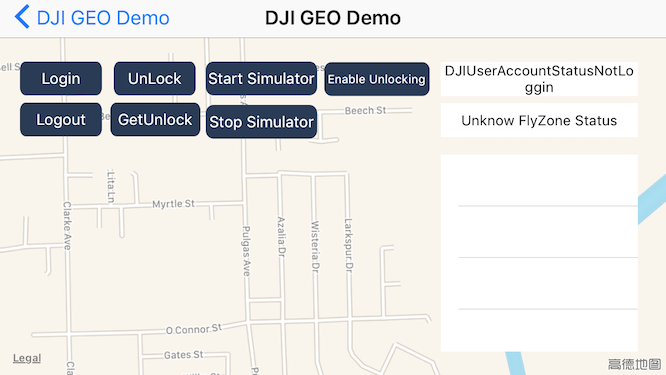
Press the Logout button to logout your DJI account.
On the upper right corner of the screenshot, you can check the loginStateLabel's info for the user account status as shown below:
Start and Stop Simulator
Instead of using DJI Assistant 2 Simulator to simulate the test environment, we use the location simulation feature of DJISimulator to locate the aircraft to specific latitude and longitude coordinate. It's more convenient to test the GEO feature in the sample.
1. Start Simulator
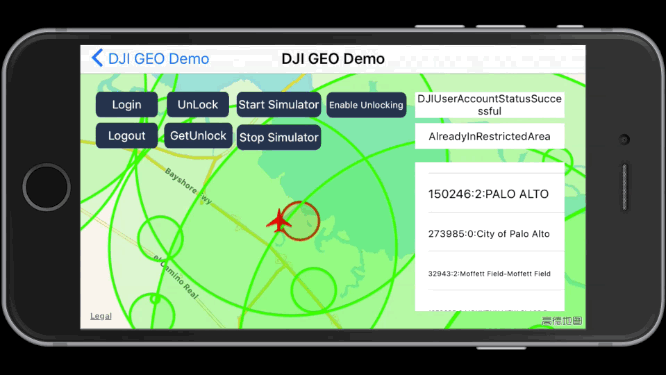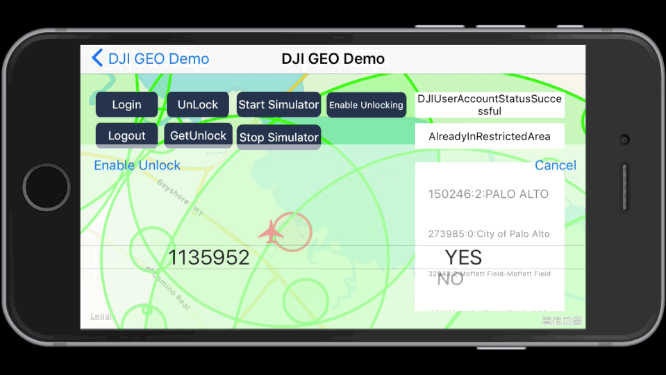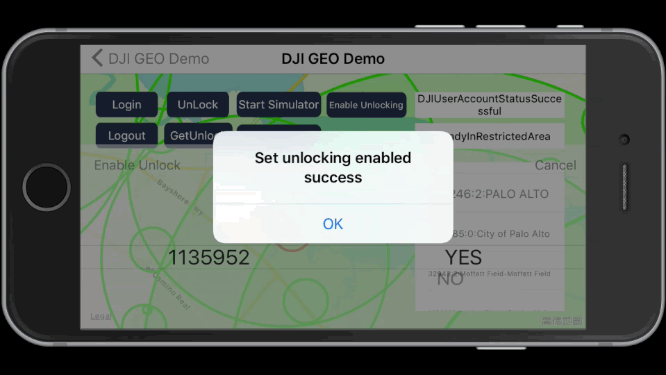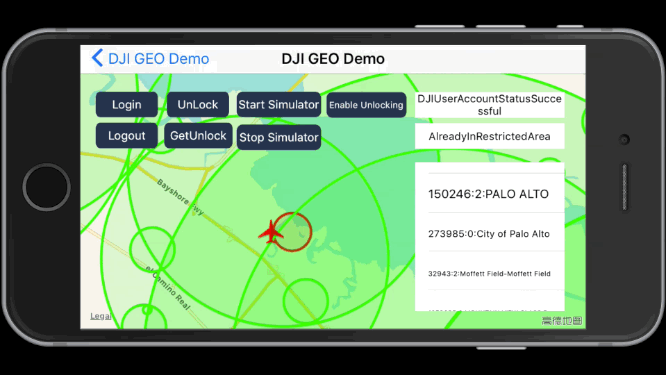
Here is the screenshot of using Start Simulator feature in the sample:
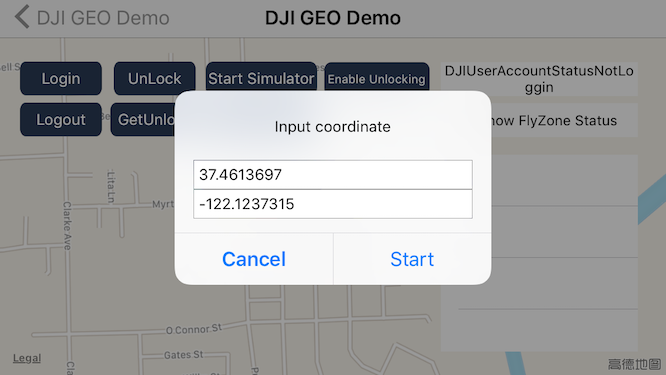
Once you locate the aircraft to the coordinate of (37.4613697, -122.1237315), you may see there are some color circles, which represent different types of fly zones.
Also the textView on the right side will show the DJIFlyZoneInformation info, includes the fly zone number, fly zone id (required in the unlock process), fly zone category and name.
At the same time, the fly zone status label's info will be updated according to the aircraft's coordinate changes.
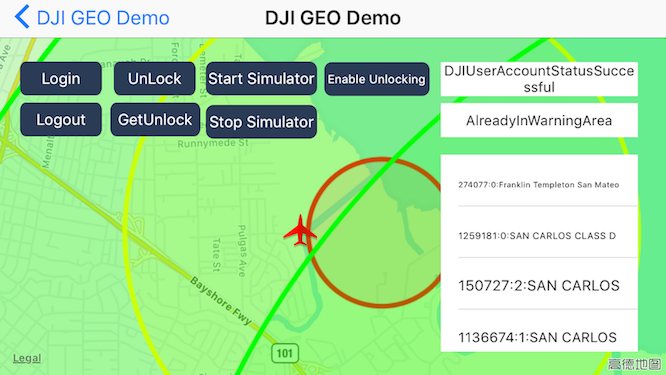
-
Yellow Circle
It represents the authorization fly zone, which will restrict the flight by default, it can be unlocked by a GEO authorized user.
-
Red Circle
It represents the restricted fly zone, it will restrict the flight by default and cannot be unlocked by a GEO authorized user.
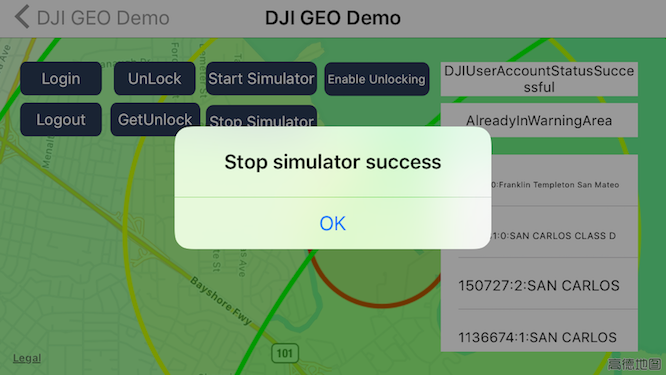
2. Stop Simulator
Press the Stop Simulator button to stop the simulator, an alert view will show as shown below:
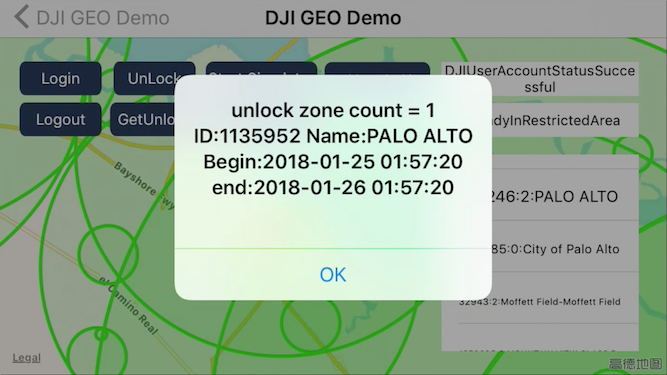
Unlock and Get Unlock Fly Zones
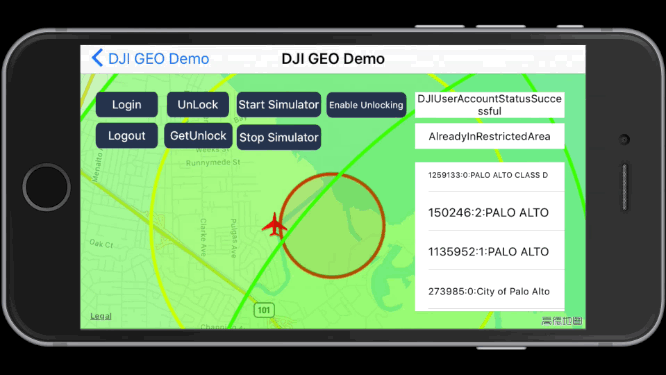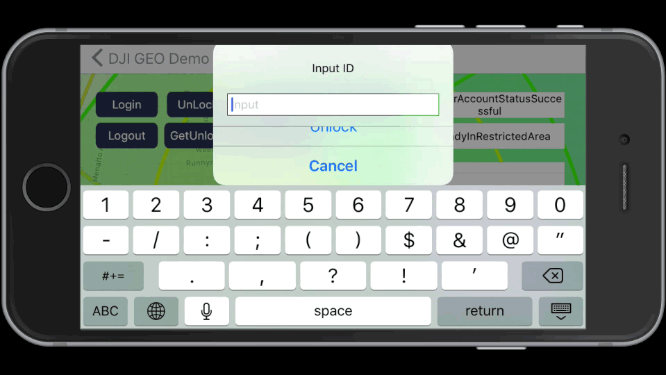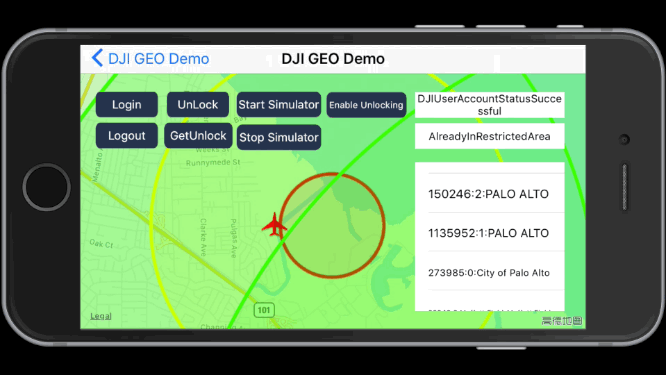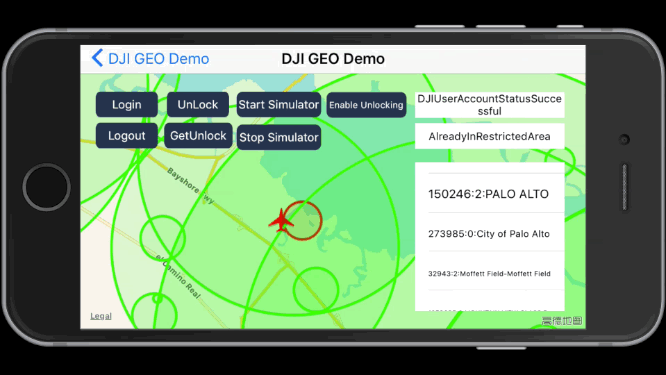
1. Unlock Fly Zone
After you login with your DJI account and locate the aircraft to the coordinate of (37.4613697, -122.1237315), you can press the Unlock button and type in the fly zone ID to unlock it.
If you unlock the fly zone successfully, you may see the yellow circle disappear and the right fly zone info are updated as shown in the following gif animation:
2. Get Unlock Fly Zone list
You can press the GetUnlock button to get the fly zone you have unlocked before as shown below:
Enable Unlocked Fly Zone
You can press the Enable Unlocking button to enable the unlocked fly zone as shown below. This is useful if the aircraft is shared between users.
Summary
In this tutorial, you've learned how to use the DJIFlyZoneManager and DJIFlyZoneInformation of DJI Mobile SDK to get the fly zone information, how to unlock authorization fly zones and how to add aircraft annotation and draw fly zone circle overlays on the map view to represent the fly zones. Moreover, you've learned how to use the DJISimulator feature to simulate the aircraft's coordinate and test the GEO System feature indoor without flying outside.
Hope this tutorial can help you integrate the GEO System feature in your DJI SDK based Application. Good luck, and hope you enjoyed this tutorial!