Building a Visual Tracking Project
This tutorial gives an example of building a visual tracking project using Guidance SDK step by step. It supports Windows and Linux.
A complete visual tracking project is already included in the demo folder. The user is encouraged to build and run the project first to get a feeling of how it would work. Then follow the instructions below to get the knowledge of how to build a Guidance SDK project from scratch.
Download and unzip SDK
Latest version of SDK is available on GitHub and then decompress it: Guidance SDK.
The content includes:
- demo: a visual tracking project by using Guidance SDK
- doc: API details
- examples: examples for USB, UART and ROS
- include: header file of Guidance SDK
- lib: library files for Windows
- so: library files for Linux
Windows
1. Create a project named “guidanceSDK_test”
Create an empty project in VS2010 in directory “demo” named “guidance_track”.
![]()
2. Add .h and .cpp to project
2.1 Add main.cpp
Add an empty main.cpp to project first.
2.2 Add DJI_utility.h and DJI_utility.cpp
Copy the thread security related files DJI_utility.cpp and DJI_utility.h to the same directory as main.cpp, and add them in vs2010. DJI_utility.cpp and DJI_utility.h can be found both in SDK/demo and SDK/examples.
- Find DJI_utility.h and DJI_utility.cpp in demo/sdk_tracking_camshift/camshift.
- Copy DJI_utility files to project path, and add DJI_utility files to the project:
![]()
![]()
2.3 Configure the Include and Library path
Now we need to configure DJI_guidance.h, DJI_guidance.lib and OpenCV related path. DJI_guidance.h is in include, DJI_guidance.lib is in lib. DJI_guidance.lib in lib/2010/x86 is going to be used here as we will run programs in Release | Win32 mode.
- Find the configuration of Visual Studio 2010, which is Release | Win32:
![]()
- Find DJI_guidance.h is in include and copy to project directory.
- Find DJI_guidance.lib in lib/2010/x86 and copy to project directory.
- Add OpenCV related header and library path to the project.
To simplify the configuration, we can copy the property sheets “use_opencv_release_vs2010_x86.props” “use_Guidance_vs2010_x86.props” in demo/sdk_tracking_camshift to the solution directory and add to the new project.
- Find “use_opencv_release_vs2010_x86.props” and “use_Guidance_vs2010_x86.props” in sdk_tracking_camshift:
![]()
- Copy the property sheet files to the solution directory
![]()
- Switch the toolbar to “Property Manager” as shown below. Right-click the Release | Win32, and click the “Add Existing Property Sheet”, then add: “use_opencv_release_vs2010_x86.props” “use_Guidance_vs2010_x86.props” to the new project.
![]()
Attention: Make sure you have installed OpenCV, and set up the environment variable OPENCVROOT properly, which is used by the OpenCV property sheet.
Users can modify the property sheet to adapt to changes of the path of project. Here gives a look at the path of Include and Library of Guidance SDK.
- Include path of Guidance SDK in“use_Guidance_vs2010_x86.props”
![]()
- Library path of Guidance SDK in “use_Guidance_vs2010_x86.props”
![]()
3. Configure dynamic library
Copy the DJI_guidance.dll from SDK/lib/2010/x86 to the bin folder of our project.
![]()
4. Edit main.cpp
- Add the necessary headers to main.cpp first. DJI_guidance.h is for Guidance SDK, DJI_utility.h is for thread security, and OpenCV related headers are for image processing.
|
- Declare global variables that will be used in different threads. Image stores the data transferred and the result, g_lock provides thread security functions, g_event gives the method to respond to data transfer event, selection is declared for user to select object to track, WIDTH, HEIGHT and IMAGE_SIZE are the size of the images.
|
- Then define an object selection function using mouse, which enables users to easyly select the object to track at the beginning of data transfer.
|
- Here provides a help function, which is for showing the information of how this program works in the mode of Windows Console. User can get the help information as follows:
|
Help function prototype:
|
Since this tutorial gives a demo of camshift based tracking using depth image, users need to select object to track when the program starts with the window of “Guidance Tracking Demo”, and then the result will be shown.
![]()
- Now we define a callback function, which will be called when the subscribed data comes. Users should only write light-weight processing functions in the callback function, such as data copy, otherwise the data transfer frequency will be slowed down.
|
- Most Guidance SDK functions return an int type error code, non-zero if functions called fail, e.g. init_transfer(), start_tansfer(), which enables the user to determine the reason when error occurs. Here we write two macros, to print the error code or directly quit the program if error occurs.
- Initialization, data subscription, data transfer start, image process, data transfer release and so on in main function.
|
5. Build and Run
Make sure the environment has been set up properly.
One can click the “Build” and then “Start Debugging” after connecting and starting the Guidance.
Linux
1. Download SDK package and create a project directory
-
Download the SDK package to
~/Desktop/GuidanceSDK. -
Create a directory
~/Desktop/SDK/demo/guidance_track, and copy DJI_utility.cpp, DJI_utility.h and main.cpp created under Windows to this directory.mkdir ~/Desktop/GuidanceSDK/demo/guidance_track cd ~/Desktop/SDK/demo/guidance_track
![]()
2. Copy libDJI_guidance.so
Suppose the operating system is Ubuntu14.04 32bit. Copy the libDJI_guidance.so from so/x86 to usr/local/lib. Notice that sudo is necessary to copy these files to /usr/local/lib:
|
3. Edit Makefile
Create a Makefile in the project directory. Make sure OpenCV has been installed.
|
Code of Makefile:
|
4. Make and run
- Power up Guidance, and connect it to computer via USB.
- Make and run the project:
|
-
Draw the object box with mouse when program is running. One could see pictures as follows if everything goes well.
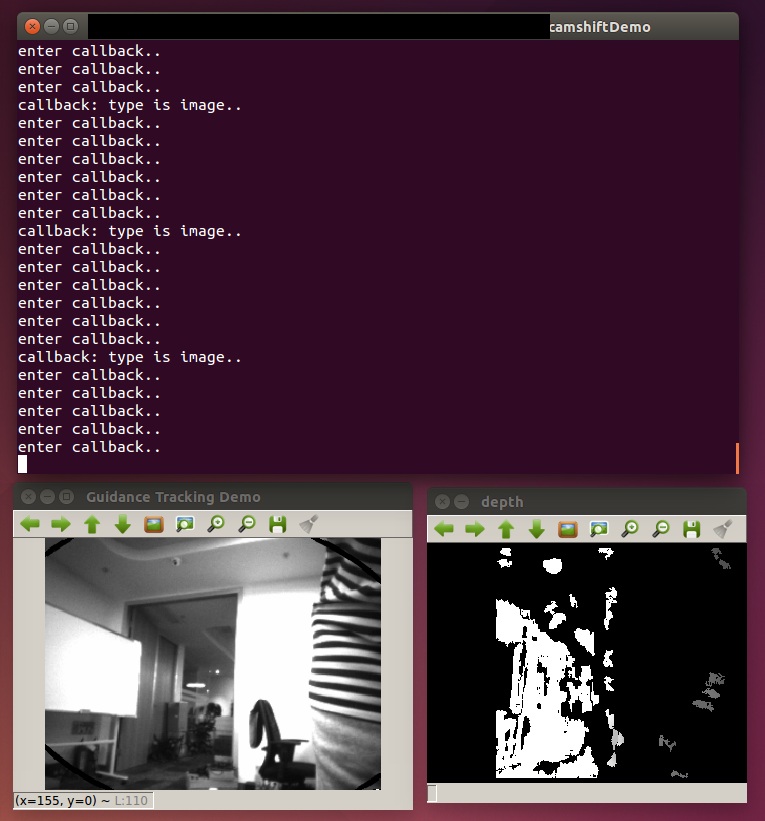
-
Type
qon keyboard will quit the program.